Table of Contents
Introduction
As cities around the world grow increasingly complex, the integration of AI and Smart Cities technology is revolutionizing urban living. The convergence of artificial intelligence with smart city initiatives is not just a futuristic concept; it’s already transforming how cities operate, manage resources, and serve their residents. This evolution towards smarter cities is driven by AI’s ability to enhance infrastructure, optimize resource management, and significantly improve the quality of life for urban dwellers.
AI and Smart Cities are reshaping urban environments in ways that were once unimaginable. From intelligent traffic systems that reduce congestion to AI-driven energy management that minimizes waste, the potential of AI in creating more efficient and livable cities is immense. This article explores the key applications of AI in Smart Cities, the myriad benefits they bring, and the challenges that need to be addressed. Additionally, we’ll take a glimpse into emerging trends that will define the future of urban living.
1. Understanding Smart Cities
A Smart City leverages digital technology to improve the efficiency of urban services and infrastructure. At the core of this transformation is artificial intelligence, which analyzes vast amounts of data, automates complex processes, and provides real-time insights. By integrating AI, cities become more responsive and capable of addressing urban challenges such as traffic congestion, energy management, and public safety.
AI’s role in Smart Cities is critical for analyzing data from various sources, such as sensors and cameras, and transforming it into actionable information. This capability allows city managers to make informed decisions that improve the overall quality of life for residents. Moreover, AI helps to streamline processes, reduce costs, and promote sustainability, making cities more resilient and adaptable to change.
2. Key Applications of AI in Smart Cities
2.1 Traffic Management
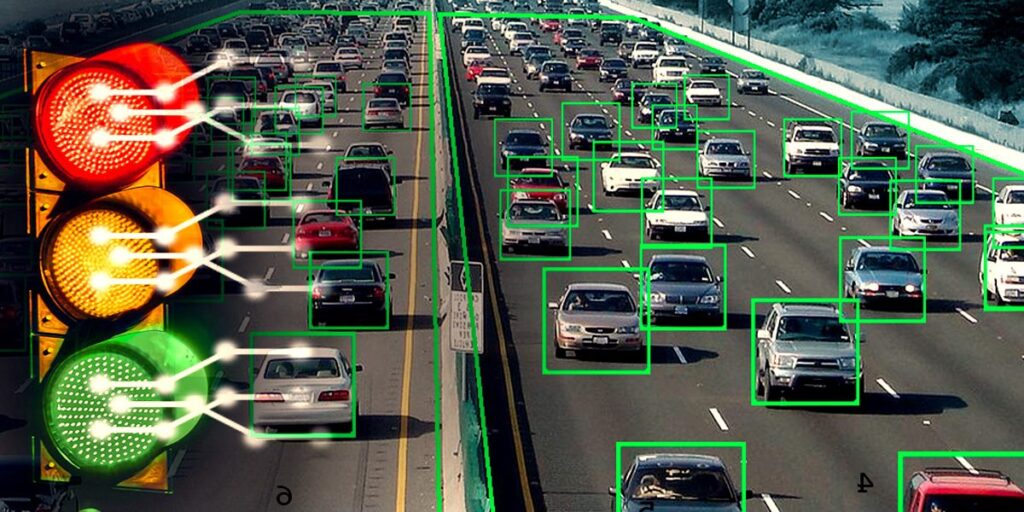
AI optimizes urban traffic flow, reduces congestion, and enhances road safety. Through the use of traffic cameras and sensors, AI algorithms analyze vehicle movements to adjust traffic signals and manage traffic patterns in real-time. This leads to smoother traffic flow, reduced travel times, and lower emissions, contributing to a healthier urban environment.
2.2 Energy Management
Smart cities rely on AI to monitor and manage energy consumption efficiently. AI systems analyze data from smart meters and sensors to optimize energy distribution, ensuring resources are used effectively. By predicting energy demand, AI helps balance supply and demand, reducing energy waste and promoting sustainability in urban areas.
2.3 Waste Management
AI enhances waste collection and disposal processes in smart cities. Smart bins equipped with sensors monitor waste levels and notify collection services when they are full. AI then optimizes collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs. This results in cleaner cities with more efficient waste management systems.

2.4 Public Safety
AI significantly improves public safety through advanced surveillance and predictive analytics. AI-powered cameras with facial recognition can identify suspects and monitor public spaces for suspicious activities. Predictive analytics help law enforcement agencies anticipate and prevent crimes by analyzing patterns and trends, making cities safer for everyone.
2.5 Environmental Monitoring
AI enables cities to monitor environmental conditions such as air quality, noise levels, and water quality in real-time. Sensors collect data continuously, and AI analyzes this information to detect anomalies and predict potential environmental issues. This proactive approach helps cities take swift actions to protect public health and maintain a clean environment.
2.6 Healthcare Services
In smart cities, AI transforms healthcare by improving diagnostics, patient care, and management. Telemedicine platforms powered by AI offer remote consultations and health monitoring. AI analyzes patient data to provide personalized treatment plans and predict potential health issues, leading to better healthcare outcomes for residents.

3. Benefits of AI in Smart Cities
3.1 Enhanced Efficiency
AI automates various city management processes, resulting in increased efficiency. This reduces operational costs and ensures optimal use of resources, allowing cities to deliver better services to their residents.
3.2 Improved Quality of Life
Smart cities enhance residents’ quality of life by providing better services and infrastructure. Efficient transportation systems, clean environments, and responsive public services contribute to a higher standard of living.
3.3 Sustainability
AI helps cities become more sustainable by optimizing resource use and reducing waste. This promotes environmental conservation and helps cities reduce their carbon footprint, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
3.4 Economic Growth
Smart cities attract businesses and investments, driving economic growth. With advanced infrastructure and efficient services, cities create a conducive environment for innovation and entrepreneurship, leading to job creation and prosperity.
4. Challenges and Considerations
4.1 Data Privacy and Security
The use of AI in Smart Cities involves collecting vast amounts of data. Ensuring data privacy and security is crucial to protect residents’ personal information. Cities must implement robust data protection measures and comply with relevant regulations to maintain trust.
4.2 Infrastructure Costs
Building and maintaining Smart City infrastructure can be costly. Cities need to invest in technology, sensors, and AI systems. Therefore, careful planning and resource allocation are essential to ensure the sustainability of these projects.
4.3 Ethical Concerns
The deployment of AI raises ethical concerns, particularly related to surveillance and bias. It is essential to establish ethical guidelines and ensure transparency in AI operations to avoid misuse and protect citizens’ rights.
4.4 Digital Divide
Not all residents may have access to digital technology. Bridging the digital divide is crucial for the success of Smart Cities, ensuring that all citizens benefit from technological advancements, regardless of their socio-economic status.
5. Future Trends
5.1 Integration of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) will play a significant role in Smart Cities. Connected devices and sensors will provide real-time data, enabling more efficient city management and enhancing the capabilities of AI systems.
5.2 Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are expected to become a common feature in Smart Cities. AI-powered self-driving cars and buses will improve transportation efficiency and safety, reducing the need for human intervention and cutting down on traffic-related incidents.
5.3 Renewable Energy Integration
As cities aim for sustainability, the integration of renewable energy sources will become a priority. AI will play a crucial role in optimizing the use of solar, wind, and other renewable energies, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a greener urban environment.
5.4 Citizen Participation
Smart Cities of the future will encourage greater citizen participation through digital platforms. Residents will have more opportunities to provide feedback, report issues, and engage in decision-making processes, making urban governance more transparent and inclusive.
Conclusion
AI is at the heart of Smart City initiatives, fundamentally transforming urban living. From traffic management to healthcare services, AI enhances efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life in cities. However, addressing challenges such as data privacy, infrastructure costs, and ethical concerns is vital. As AI technology continues to evolve, the future of Smart Cities looks promising, offering innovative solutions for the urban challenges of tomorrow.
Further Reading: For more insights into AI and its applications in urban living, check out our series on AI technologies and AI News.
FAQ Section
- What role does AI play in Smart Cities? AI enhances urban living by optimizing traffic management, energy use, waste management, and public safety in Smart Cities.
- How does AI improve public safety in Smart Cities? AI-powered surveillance and predictive analytics help monitor public spaces, identify threats, and prevent crimes before they occur.
- What are the main challenges of implementing AI in Smart Cities? Key challenges include ensuring data privacy, managing infrastructure costs, addressing ethical concerns, and bridging the digital divide.
- How do Smart Cities benefit from AI in energy management? AI optimizes energy distribution, reduces waste, and predicts energy demand, promoting efficient use of resources and sustainability.
- What future trends will shape AI and Smart Cities? Trends include the integration of IoT, the rise of autonomous vehicles, renewable energy use, and increased citizen participation.